Real-time, supply chain test marketing of new product lines
 Tuesday, March 1, 2011 at 4:36PM
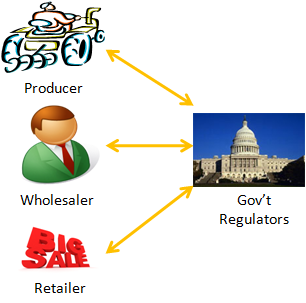
Tuesday, March 1, 2011 at 4:36PM Assume that a retailer, a class of beef product pre-retailers (i.e., wholesalers, processors and vertically integrated operators), and a class of consumers are all multi-tenant members of a centralized personal data store for sharing supply chain information.
I gave an example of a multi-tenant Food Recall Data Bank in an earlier blog entitled Consortium seeks to holistically address food recalls. At the time I wrote this earlier blog I vacillated between calling it what I did, or calling it a VRM Data Bank. I refrained from calling it the latter because while the technology application is potentially very good for consumers (i.e., food recalls tied to point of sale purchases) it still felt too much like it was rooted in the world of CRM. For more about the VRM versus CRM debate see The Bullwhip Effect.
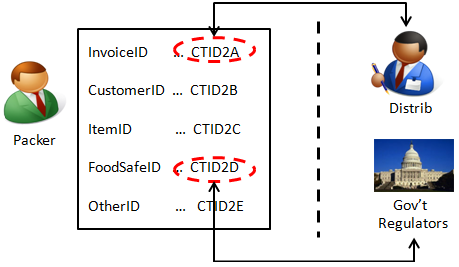
Below is a technology application whereby supply chain tenants may register their CPA informational objects with permissions and other instructions for how those objects may be minimally accessed, used and further shared by and to other supply chain participants. What one then has is what may more appropriately be called a VRM Data Tenancy System (VRM DTS).
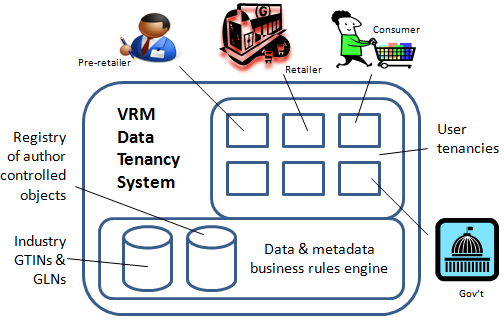
So what can one do with this architecture? How can it get started in the marketplace of solutions? A reasonable beginning point is with real-time, supply chain test marketing of new food product lines. And by supply chain test marketing, I mean something clearly more than just consumer test marketing. What I am describing below is multi-directional, feedback loop for:
- test marketing a new consumer product line for the purpose of driving retail sales, and
- concurrently generating procurement and wholesale interest and support from pre-retailers.
Assume that a retailer has been receiving word of mouth consumer interest in a particular beef product class (e.g., "ethically raised" beef products). Assume that pre-retailers have heretofore not been all that interested in raising, processing or purchasing "ethically raised" meat products for wholesale.
An initial "test market" object is authored and registered by the retailer for polling consumer interest via asynchronous authoring by individual consumers of their store outlet preferences, likely beef product quantity purchases of the new product line per week, etc. This object is revealed to a consumer class via their tenancies in the VRM DTS. The object is concurrently revealed to a class of pre-retailers via their tenancies, too. Each consumer is anonymous to the other consumers, and anonymous to the pre-retailers. Each pre-retailer is anonymous to the other pre-retailers, and anonymous to the consumers. But each consumer, as is each pre-retailer, is nonetheless privy to the consumers' real-time poll and the pre-retailers' real-time poll. The retailer watches all, being privy to the actual identities of both consumers and pre-retailers, while at the same time the retailer’s customer and pre-retailer client lists remain anonymous.
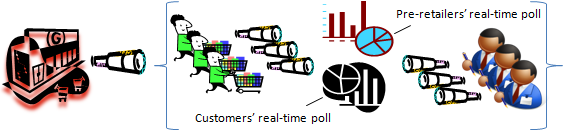
With this kind of real-time sharing of information, one can begin to imagine a competitive atmosphere arising among the pre-retailers. Furthermore, there is no reason the retailer's object could be further authored by the retailer to solicit real-time offers from the pre-retailers to procure X quantities of the beef products for delivery to identified outlets of the retailer by dates certain, in the same specific beef product class, etc. And there's no reason the "test market" object could not be further used to finalize a procurement contract with one or more pre-retailers ...
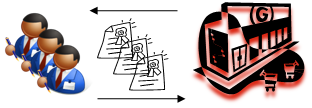
... which at the moment of execution shares real-time, anonymized information over to consumers as to dates of delivery of X quantity of beef products at identified retail outlets.

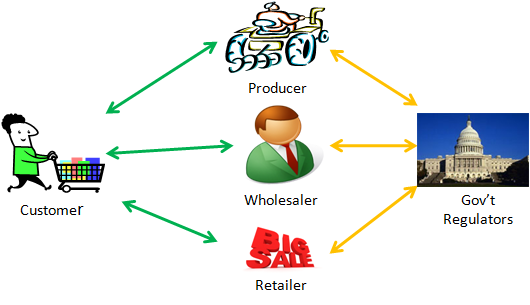
The "test market" object could be further designed for the consumer class to asynchronously provide real-time feed-back to the retailer regarding their experiences with the purchased product, and to perhaps do so even back to the pre-retailers based upon GLNs and GTINs. Depending on the retailer's initial design of the "test market" object, this consumer feedback to pre-retailers may be anonymous or may specifically identify a branded product. And, because food safety regulators are seeking "whole chain" traceability solutions, the government can be well apprised with minimal but real-time disclosures.
The dynamic business model for employing a VRM DTS includes greater supply chain transparency (increased, ironically, with consumer and pre-retailer anonymity), food discount incentives, real-time visualizations, new data available for data mining, and new product outlets for pre-retailers who have not previously provided products to the retailer. Perhaps most significantly there is the identification by the retailer of best of breed pre-retailers and loyal, committed consumers via an “auction house” atmosphere ...

... created from the sharing of real-time, sometimes anonymous information, between and among the pre-retailers and consumers.
 Steve Holcombe
Steve Holcombe
Consumer Control: Coming To A Store Near You
Alessandra Lariu
7 November 2013
Alessandra Lariu, co-founder of SheSays, argues that people if take charge of their data, it could fundamentally change advertising dynamics
 Steve Holcombe
Steve Holcombe
 Steve Holcombe | Comments Off |
Steve Holcombe | Comments Off |  chain,
chain,  crm,
crm,  distribution,
distribution,  food,
food,  marketing,
marketing,  retail,
retail,  supply,
supply,  test,
test,  wholesale in
wholesale in  Business Models,
Business Models,  CPA,
CPA,  Identity,
Identity,  Informational Objects,
Informational Objects,  Intellectual Properties,
Intellectual Properties,  Supply Chains,
Supply Chains,  VRM,
VRM,  Whole Chain
Whole Chain